CHAPTER 1 ‘WHAT IS THE EUROPEAN UNION?’
EXERCISE 1 WHO IS A MEMBER OF THE EU?

EXERCISE 3 WHAT DO THE EU’S VALUES AND PRINCIPLES MEAN IN PRACTICE?
| A country … | (A) can join the EU |
(B) can’t join the EU |
|---|---|---|
| 1. that does not have freedom of the press | NO | YES |
| 2. that applies the death penalty | NO | YES |
| 3. that allows its citizens to protest against the government | YES | NO |
| 4. in which the parliament is elected on a regular basis | YES | NO |
| 5. in which the army determines policy and may even intervene in internal affairs with military power | NO | YES |
| 6. in which people are considered innocent until their guilt has been established by a court | YES | NO |
| 7. in which there is only one party which is always in government | NO | YES |
| 8. which protects minorities, even when the majority is against them | YES | NO |
CHAPTER 2 ‘HOW DOES THE EU WORK?’
EXERCISE 7 WHO DOES WHAT IN THE EU?
| Who …? | European Parliament | European Council | Council of the European Union | European Commission | European Court of Justice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. makes proposals for EU laws | NO | NO | NO | YES | NO |
| 2. approves EU laws | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO |
| 3. consists of (only) one representative/member per EU country | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 4. is directly elected | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO |
| 5. manages the budget | NO | NO | NO | YES | NO |
| 6. represents the interests of the people | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO |
| 7. represents the interests of EU countries/their governments | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 8. represents the interest of the EU as a whole | NO | NO | NO | YES | NO |
| 9. decides on the interpretation of EU laws | NO | NO | NO | NO | YES |
| 10. defines the general political direction of the EU | NO | YES | NO | NO | NO |
EXERCISE 8 LAW-MAKING IN THE EU

EXERCISE 9 WHO IS WHO?
You now know a lot about the European institutions, but do you know the names and faces of the people leading them? Do you know who is the current:
- President of the European Parliament (https://europa.eu/!9dR4kW).
- President of the European Council (https://europa.eu/!wW73CM).
- President of the European Commission (https://europa.eu/!Xd39kv).
- High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission (https://europa.eu/!g9kXjH).
 Roberta Metsola
President of the European Parliament
Roberta Metsola
President of the European Parliament
 Charles Michel
President of the European Council
Charles Michel
President of the European Council
 Ursula von der Leyen
President of the European Commission
Ursula von der Leyen
President of the European Commission
 Josep Borrell Fontelles
High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission
Josep Borrell Fontelles
High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission
CHAPTER 3 ‘HOW IS THE EU RELEVANT TO YOUR DAILY LIFE?’
EXERCISE 12 WHICH COUNTRIES ARE IN THE EURO AREA?
- EUROAustria
- EUROBelgium
- NOBulgaria
- EUROCroatia
- EUROCyprus
- NOCzechia
- NODenmark
- EUROEstonia
- EUROFinland
- EUROFrance
- EUROGermany
- EUROGreece
- NOHungary
- EUROIreland
- EUROItaly
- EUROLatvia
- EUROLithuania
- EUROLuxembourg
- EUROMalta
- EURONetherlands
- NOPoland
- EUROPortugal
- NORomania
- EUROSlovakia
- EUROSlovenia
- EUROSpain
- NOSweden

EXERCISE 14 WHAT DOES FREE MOVEMENT MEAN FOR YOU IN PRACTICE?
| Examples | Free movement of people | Free movement of goods | Free movement of services | Free movement of capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. I can buy a second-hand car abroad and take it back home without paying customs duties. | NO | YES | NO | NO |
| 2. I can travel anywhere I like within the EU. | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| 3. I can study in another EU country. | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| 4. My parents can have their bathroom renovated by a tiler from another EU country. | NO | NO | YES | NO |
| 5. My parents can send money to me, without any extra charges, in the country where I am studying. | NO | NO | NO | YES |
| 6. I can work in another EU country. | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| 7. I can buy goods online from another EU country without paying customs duties. | NO | YES | NO | NO |
EXERCISE 15 EUROPEAN LABELS
EU laws have put strict rules in place for the labelling of food, drinks, cosmetic products and electronic appliances. Some labels help protect consumers, while others let them know about certain characteristics of the product. For example, there are labels to indicate which products are organic or energy efficient. Without proper labelling, a product will not be allowed onto the market.
 The CE marking is a safety label, showing that the product complies with EU health, safety and environmental standards.
The CE marking is a safety label, showing that the product complies with EU health, safety and environmental standards.
 The EU ecolabel is awarded to environmentally friendly products and services. It is a voluntary scheme that was introduced in 1980 by EU law.
The EU ecolabel is awarded to environmentally friendly products and services. It is a voluntary scheme that was introduced in 1980 by EU law.
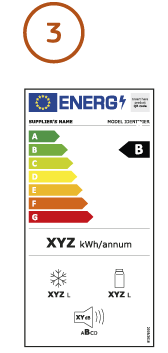 The EU energy label tells you how energy efficient an appliance is on a scale from A to G. A (green) is the most energy efficient and G (red) is the least energy efficient. A brand new version of this label was introduced on 1 March 2021 for certain product categories (fridges, freezers, dishwashers, washing machines and television sets). Other products will follow in the coming years.
The EU energy label tells you how energy efficient an appliance is on a scale from A to G. A (green) is the most energy efficient and G (red) is the least energy efficient. A brand new version of this label was introduced on 1 March 2021 for certain product categories (fridges, freezers, dishwashers, washing machines and television sets). Other products will follow in the coming years.
 The EU organic logo tells you that the product meets EU rules for the organic farming sector. For processed products this means that at least 95 % of the agricultural ingredients are organic.
The EU organic logo tells you that the product meets EU rules for the organic farming sector. For processed products this means that at least 95 % of the agricultural ingredients are organic.
 The three EU quality logos indicate characteristics of food products derived from the geographical location in which they are produced or from their traditional composition or production method.
The three EU quality logos indicate characteristics of food products derived from the geographical location in which they are produced or from their traditional composition or production method.